Engeneering
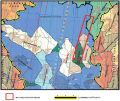
The article is devoted to a modern seismic inversion model. The spatial distribution of impedance is simulated using a synthetic well tie. A low-frequency background model is built as well as an acoustic impedance cube. Density and sonic log data are balanced. The study conducted both an analysis of petroelastic properties and a dynamic analysis. Guidelines for drilling locations are given. The method used takes into account the geological data based on a structural model for seismic horizons.
The article presents a model of a spine position monitoring system that can gather posture statistics, analyze them using neural networks, and provide the user with personalized posture training instructions. The study focuses on a mobile app as it is user-friendly and simplifi es system development. As a result, the requirements for the system’s structure and operation were identifi ed and described
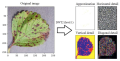
The article demonstrates a method that combines the wavelet transform and machine learning methods to classify plants health using colored digital images. The input data for classifi cation is comprised of a built vector of Haralick texture features. The software was developed via the Python programming language to classify digital images with the multilevel discrete Daubechies wavelet transform and methods of classifi cation for machine learning, particularly classic logistic regression and perceptron. The effi ciency of this method for solving the problem of multiclass image classifi cation is demonstrated. The study concludes and assesses the prospects of the method.
The article examines issues of modeling computation processes that help assess the probable capabilities of the software used to negatively affect the operation of various types of human-machine systems, including those with artifi cial intelligence. Given its aggresive behavior, a numerical experiment analyzed software that provides intelligent support to assistant robots for teaching staff and implements certain functions in the smart home’s computation complex. The experiment’s fi ndings raise a number of issues, which are discussed. The study demonstrates an approach for highlighting a set of machine programming language statements capable of producing general and special software bugs that affect the information environment and appropriate operation of smart home components. Guidelines for grouping a set of aggressive properties
are given based on the specifi cs of the software in use.
The reason behind studying the category of effi ciency lies in the number of approaches, methods, types of defi nitions, interpretations in various fi elds; possibilities and challenges in decision-making; and the infl uence of subjective factors in particular approaches and methods. All of this enables the search for ways to improve the performance effi ciency of a service-oriented enterprise by developing an information system with an algorithm for detecting signifi cant factors. The study aims to develop an algorithm for detecting factors that can help an enterprise to improve its effi ciency. An algorithm for detecting factors that increase the performance efficiency of a service-oriented enterprise was developed to solve the problem. The algorithm is based on data collected and processed by the Federal State Statistics Service on factors that limit the operation of such enterprises and indicators that dynamically demonstrate their performance. The expert survey fi ndings, which included fi ve approaches to assessing efficiency and considering the specifi city of such activity, were applied.
Management as well as the use of software for scheduling the project company’s strategy are vital components of an organization’s economic sustainability. When working on a project, modern managers frequently employ visual aids such as task diagrams. The Gantt chart is a highly effective type of diagrams. Many project companies now include software products for designing Gantt charts as a key tool in their technical scope. The article presents the results of a study using the Choice («Vybor») decision support system. Thomas Saaty’s mathematical method of analytic hierarchy process implies the selection of the most favorable choice in decision-making. Using the analytic artifi cial intelligence system, the choices were ranged in a form of software products for building Gaant charts, and the most effective software decision was selected.
The article describes an algorithm for calculating numerical estimates of the parameters of a simple nested piecewise linear regression using mixed estimation. The algorithm aims at simultaneous identifi cation using methods of least modules and antirobust estimation, both of which operate on certain subsamplings from the initial sampling. The approach comes to solving the problem of linear Boolean programming. A numerical problem has been solved.
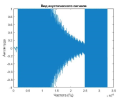
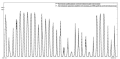
The article demonstrates an approach for acoustic signal processing under conditions of unauthorized operation on the main pipeline. A case study included tests that simulated illegal pipeline tie-ins using metal pipe drilling. In the course of the study, acoustic signals were recorded and processed using the Fourier transform method. The fi ndings revealed the apexes of common frequencies for each test. The study aims to advance the protection of long-distance high-priority facilities from illegal actions by detecting any threat based on the common apexes of frequencies recorded during acoustic signal processing, as well as to improve the timely reporting of security services.
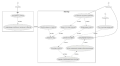
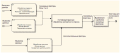
The forecasting of electric power generated by a solar power plant enables effective and safe control over electric networks which integrate a cluster of solar power plants. Penalty rates for the purchase of solar power at the day-ahead market, which deviates by more than 5 % of the maximum capacity of solar power plants from the provided hourly model of the day-ahead market of solar power generation, update the accuracy of the day-ahead market model through effective intelligent systems for forecasting solar power generation. It has been found that there is no accessible software for successful forecasting of solar power generation; the advisability and relevance of designing such software with an intelligent system have been shown based on the fi ndings of the examined existing software. The study developed, tested and implemented an intelligent system of indirect forecasting of solar power generation in the form of computer software designed based on a modifi ed fuzzy neural network with an attention mechanism. A class diagram and a block-modular architecture for computer software that implements an intelligent system of indirect forecasting of solar power generation were developed in UML notes using the Microsoft Visio CASE tool. A block-modular architecture provides the fl exibility of computer software. The computer software implementing an intelligent system of indirect forecasting for solar power generation was tested for effectiveness, robust results, and the advisability of its application for building a day-ahead market model. The SCADA database of a solar power plant can be easily integrated with an intelligent system of indirect forecasting of solar power generation.
Physics and Mathematics
The article describes an experiment of a surface tension on the air ‒ saline interface using a highly sensitive rotating drop method conducted on the SDT tensiometer of the KRUSS company. The surface tension isotherm was estimated at +20 °С in concentrations of 0 to 25 %. The temperature dependency of the surface tension coeffi cient was determined for various concentration readings within the range of +20 to +70 °С. The temperature coeffi cient of the surface tension (α) was estimated as 0.18 mN/(m×K).
The article studies the effectiveness of various statistical tests for heteroscedasticity in a model. A research design and a principle for building synthetic data with various types of heteroscedasticity are described. The fi ndings of an analysis are given. The most effective tests for detecting homo- and heteroscedasticity are determined. A classifi cation trees mechanism is applied to identify the most effective tests according to the sampling properties, and such pattern is demonstrated. In applied studies, there is a need to carry out further research aimed at detecting the most suitable statistical test based on the given data properties. In addition, it is concluded that each considered test fails for different types of heteroscedasticity. Thus, it is necessary to conduct further theoretical studies in the fi eld as well as design new approaches for detecting various types of heteroscedasticity.