Engeneering
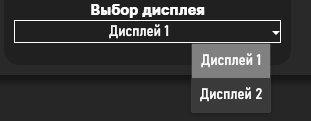
This article presents software for recording audio and video using the NAudio and Accord.NET libraries. The program is developed on the Visual Studio 2022 platform using the C# WPF programming language. The main objective of the work is to create an accessible and efficient tool for recording the computer desktop screen. The research methodology includes an analysis of the technical aspects of software development and experimental testing of the developed system. The results reveal that our system has a simple interface, flexible settings, and provides high-quality audio and video recording. In its approach to selecting a display for recording and capturing the desktop screen, the program is unique and provides flexible user options.
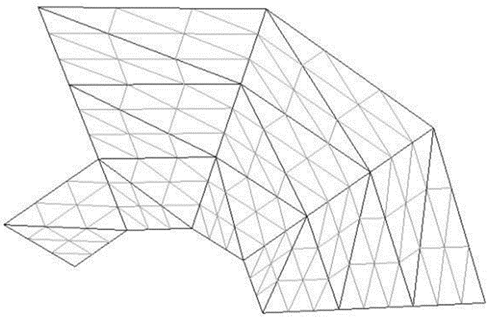
The integration of computer technologies in all spheres of human life, casual and professional, is becoming more and more relevant at present. In this regard, rapid development of new means and methods of problem solving through the use of digital and information technologies occurs. One of the most topical spheres of development is computer geometry. Nowadays, there is a number of problems to be solved in this area, one of which is triangulation of plain domains by grinding, defined by a system of inequalities. The main purpose of the presented article is the development and software implementation of a triangulation algorithm based on the grinding method for a plain domain defined by a system of inequalities. This work analyzes various triangulation algorithms, including the algorithm of grinding of a plain domain defined by a system of inequalities. This work considers the application’s function scheme and its implementation. The theoretical significance of the study is the exploration of general concepts, properties, and algorithms of triangulation. The practical significance of the study consists in giving a software implementation of the algorithm of plane domain grinding. Researchers can use the results of this work in subsequent studies that use triangulation for plane domain grinding.
This article continues the authors’ research in the field of human-machine interaction. The work addresses the problem of recognizing the human emotional state in the process of labor activity. Using Deep-Face, software for identifying and classifying emotions is implemented. The approbation of the software has shown the possibility of its implementation for the human functional state identification.
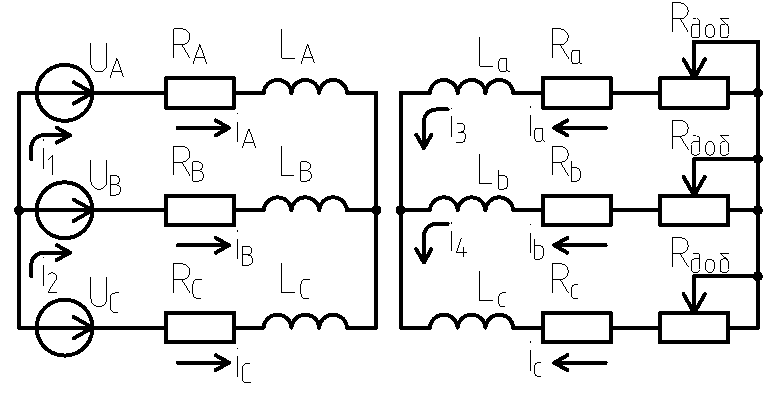
Induction motors are key elements of many electric power systems, especially electrification systems for technological installations of oil and gas facilities.Improving the efficiency, reliability and safety of induction motors requires accurate modelling of electromagnetic and mechanical processes, especially in transient conditions and with supply voltage asymmetry. This article presents a review of the mathematical model of a wound rotor induction motor based on the mesh-current method for interphase voltages. The model considers the influence of supply voltage asymmetry and provides an opportunity to study transients occurring in various operating modes, including starting. Using a proper model will enable prediction of machine main element service life and improved fault diagnostic work quality. This study provides modeling results, compares them to existing models, and demonstrates the effectiveness of the proposed method.
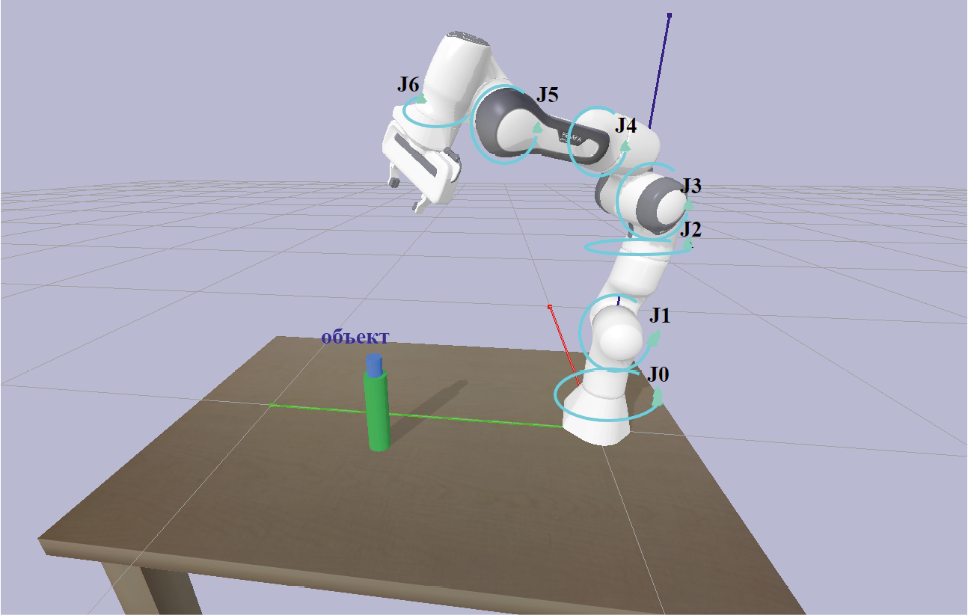
The article describes the solution to the inverse kinematics problem for object grasping with the 7-DOF Franka Emika Panda manipulator, implemented with computer vision. In proposed solution, the robotic arm operates in a physical simulation environment, utilizing reinforcement learning algorithms from machine learning, supplemented by computer vision algorithms for geometric structure-based target localization and
training, enabling the implementation of the entire algorithmic process. The process of problem solving, constructing the corresponding environment, and analyzing the outcomes of the integrated algorithm, which incorporates neural networks, demonstrates its capability to effectively solve complex inverse kinematics tasks. This cost-effective modern technique applies widely to similar tasks with other robotic manipulators.
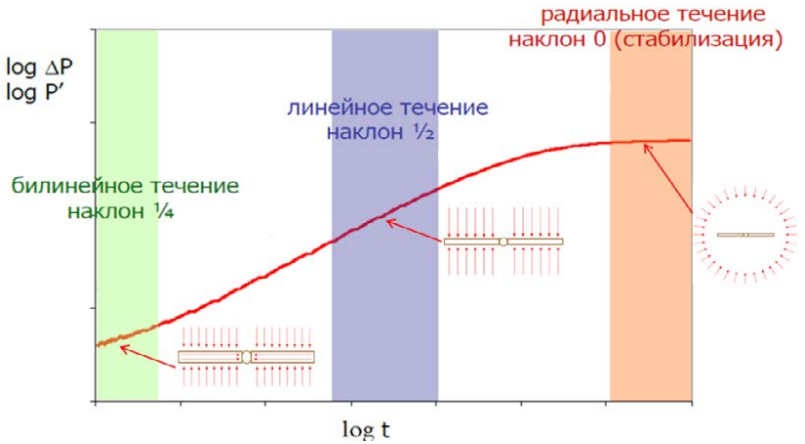
Nowadays, the majority of oil and gas companies’ fields have commercial oil reserves and need efficient methods of developing hard-to-recover oil reserves. The basic criteria for reserves to become hard-to-recover ones are low reservoir permeability (about 40%), low productivity and high oil viscosity. The practical value of this work is the contribution to hydrodynamic studies of wells in low-permeability reservoirs by detecting unstable autonomous hydraulic fracturing, implementation of an approach to predict reservoir pressure in the absence of radial filtration, as well as determination of the optimal study time.
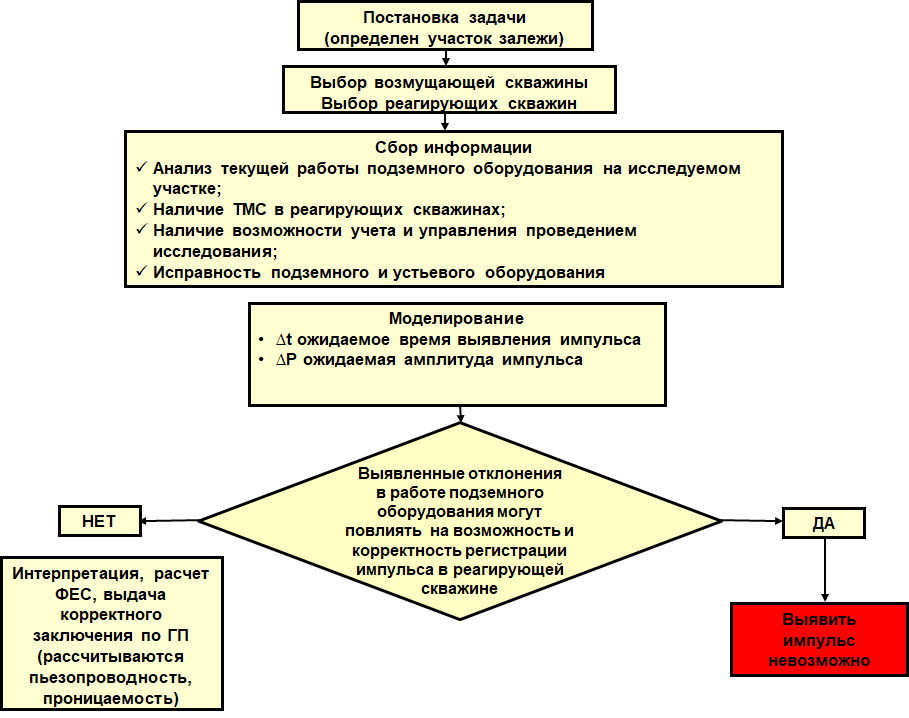
Information on the structure of the deposit and pressure communication between wells is required to control development and plan geological and engineering operations. Pressure transient test using the pulse-code is traditionally used to record the generated pressure pulse in shutdown observation wells, which leads to reduced rates of oil production. Pulse-code test method has not been applied in operational wells in the world practice. The article considers the main problems arising in the process of pulse-code testing on the operational well stock, as well as provides possible solutions to the potential problems occurring in the process of the study and factors that interfere with the successful conduct of the work.
Physics and Mathematics
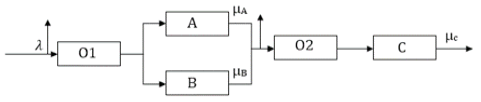
The article focuses on systems with a fixed maximum number of demands in the queue. This means that it is necessary to take into account not only the queue but also its finite capacity, which contributes to the complexity of analyzing such systems. The introduction of such limits potentially enables more realistic functional models reflecting actual operating conditions of queuing systems. Understanding the basic concepts of queuing theory contributes both to structure of the study and further research opportunities. Researchers review existing models and systems to find their strengths and weaknesses. Comparative analysis provides opportunities to adapt proven solutions to new conditions and to avoid the mistakes of past research.
The article describes the modeling of population dynamics based on predator–prey model, which considers simultaneous presence of several predator and prey species in system, as well as random changes in the amount of vegetation due to anthropogenic and biotic factors. The model incorporates vegetation as a food source for prey, resulting in a more realistic and comprehensive model. Population over time graphs and phase portraits of the system provide visualization of the modeling results and highlight key patterns. Such programs are excellent tools for teaching students, enabling them to practically apply theoretical knowledge, analyze data, and draw conclusions about population dynamics in ecosystems.
The article provides a brief review of publications on the implementation of nonlinear model forms in mathematical modeling of complex technical and socio-economic objects. Specifically, the following are considered: the dynamics of a nonlinear system with two degrees of freedom, consisting of a grounded
linear oscillator connected to a light mass by a substantially nonlinear and nonlinearizable stiffness; the description of a new cybernetic structure that can help in understanding the specifics of timely deployment of
recurring social phenomena; a new mathematical model for managing cyclical unemployment; configuration
of several renewable energy systems in an eco-industrial park, an economic and mathematical model of production planning that takes into account its scale and the release of defective products. Homogeneous nested piecewise linear regressions with alternating min and max functions are studied. The tasks of calculating parameter estimates by minimizing the sums of absolute values of approximation errors are reduced to linear Boolean programming problems. The obtained optimal values of the Boolean variables of the problem reveal the order of external minimum and internal maximum in the considered nested models. A numerical illustrative case is solved.