Engeneering
Oil and gas companies carry out routine and major repairs of wells using mobile drilling complexes equipped with top drive systems (TDS) in order to increase the fl ow rate of oil and gas wells. Statistical data on the operation of more than sixty TDSs in the fi elds of Western Siberia were collected and analyzed. The TDS’s main reliability indicators, such as the probability of failure-free operation and the failure rate, were calculated. The fi ndings can be used to improve drilling equipment maintenance and repair procedures. The insuf fi cient level of reliability of the TDS elements, along with intense operating conditions in the fi elds of Western Siberia, causes failures and halts the entire technological process of well repair, necessitating the need for repair and renewal operations. The fi rst priority of oil and gas companies lies in increasing the TDS reliability based on the high requirements for the reliability of drilling equipment operated at hazardous production facilities, as well as driven by the purpose of continuous operation on routine and major repairs of wells.
The article is devoted to the problem of estimating logistic regressions where the explanatory variable has only two values, 0 and 1. The predicted values of the explanatory variable of the estimated logistic regression are interpreted as the probabilities of the occurrence of some event. As a result, such models are widely used to solve classifi cation problems. In practice, the maximum likelihood estimation, which is implemented in many modern statistical packages, is mainly used to estimate logistic regressions. One of its disadvantages, for example, is that it does not provide unique estimates when grouping objects into two separate classes. The study proposes a new method for estimating logistic regressions. Conventionally, it can be divided into two stages. The fi rst stage consists of solving a specially formulated linear programming problem. As a result, the weighting coeffi cients of the linear combination of explanatory variables are found. In fact, classifi cation is already carried out at this stage. The second stage is to calibrate the probability scale. Computational experiments were carried out based on a real sample of volume 100. The new method has proven its effi ciency when objects are completely separable into two classes. In addition, in terms of the number of correctly predicted cases, the new method was never inferior to the maximum likelihood estimation, and even surpassed the latter in one of the experiments.
The study classifi es eight types of plants’ diseases using an adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS). Haralick texture features obtained from plants’ images are applied as input data for a system. A hybrid algorithm consisting of a backward propagation of error and a gradient descent performed the ANFIS training. The ANFIS effi ciency was assessed on a test set through calculating accuracy, comprehensiveness, and the F1 score. The indicators obtained by this method were compared with other modern classifi cation methods.
The study discusses a manual method for evaluating words and their sentiment analysis in order to compile a sentiment dictionary. To evaluate the emotional coloring of words, a method of modeling respondents’ evaluations of words using the best-worst-scaling questionnaire is proposed. The modeling method depends on the reference dictionaries, which help determine the statistical probabilities of the expected answer choice for a given question of the questionnaire. The human factor in the selection process can be considered by introducing an error coeffi cient. The implementation of this method allows detecting the infl uence of word distribution on evaluation results, as well as the minimum number of respondents required to gather suffi cient results in comparison with the reference dictionary.
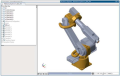
The study describes steps to solve the direct kinematic problem for a six-unit robot manipulator, the FANUC Robot M-20iA/35M. The problem solving is based on modern solid CAD modeling technologies combined with a physical modeling environment, as well as Simulink’s SimMechanics multi-unit spatial mechanisms. Simulink’s SimMechanics environment is used for visualizing the dynamics of the manipulator’s operating component. The manipulator’s matrix equation can then be used for solving the inverse kinematic problem.
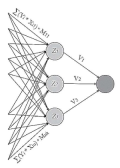
The article proposes a method for constructing a neural network architecture to solve the problem of classifying users based on their comments posted in open sources. The backward propagation of error is used to train a neural network. The training data was pre-marked, and then sampled into three groups: training, validation, and test. Customers’ reviews were pre-processed before being submitted to the network. The constructed model was implemented using special layers of words classifi ed into specifi c groups. Based on the obtained output value of the constructed network, it is possible to determine which category certain customers should be assigned. Thus, the company will be able to effectively apply targeted advertising to the identifi ed target group of consumers.
The article proposes a method that will help identify blind spots in software testing. Common problems in software testing and methods for their solution are described. A method to detect a problem is presented. The study also demonstrates an example of implementing this method.
The introduction of the automation and management principles for pharmacists’ activities using information systems is an effective way to increase profi ts and strengthen pharmacy profi tability. Companies use machine learning algorithms to adjust their strategy, study customer reviews about their organization through feedback analysis, and improve the company’s image. However, a signifi cant amount of pharmacists’ time and effort goes into the manual processing of incoming reviews. The article proposes automating the processing using the naive Bayes classifi er algorithm, which is implemented in Python. To train the classifi er, the authors created their own corpus of labeled review texts with two categories, with the total number of reviews being about 500. A parser written in Python was used to search for reviews. The following steps were taken during the preliminary processing of the reviews’ text: lemmatization, elimination of punctuation, the text’s letter conversion to lower case, tokenization, stop words removal, and text vectorization using the bag-of-words model. According to the numerical experiments carried out, the classifier’s highest accuracy was achieved with an 80/20 ratio of training and test samples that did not include stop words. When using a classifi er, analyzing 100 reviews takes 8 times less time than manual reading. The classifi er itself can be presented as a separate application or as a module within an information system. Thus, the increasing number of positive reviews is an indicator of the company’s effi cient performance as well as the number of satisfi ed customers. The growth of its image will strengthen customers’ loyalty to the company, resulting in greater sales.
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in no-code automation tools for business processes in the IT industry. Over the last fi ve years, investments in no-code platforms have crossed one billion dollars. The study focuses on the analysis of these technologies in the context of small and large businesses. However, the issue of replacing traditional development remains. The study aims to determine who benefits from using no-code and who benefi ts from traditional development. The research is relevant since companies have limited resources. Methods include effi ciency analysis and comparison of implementation results. The advantages of no-code include speed, cost, and low risks, but it is dependent on the software solution and requires programming skills. The study calls for a balance between the use of no-code and traditional development to maximize benefi ts. Based on the research, it is established that no-code and low-code development are less effective without traditional programming and will be more effective for implementation in companies that already have a team of IT specialists.
The study discusses such an important aspect of computer vision in technical vision systems as object recognition features formation. Such systems, which are widely applied in a variety of industries, allow for the rapid acquisition of a vast amount of information. At the same time, information about the observed objects’ properties, which often include movement, as well as the geometric parameters of their shape, is collected. The authors propose using object recognition features, which are based on orthoexponential functions and which retain information about the studied object’s shape. Examples of calculated complex values of the shape matrix’s elements are presented for some regular geometric shapes’ contours. The shape matrix is obtained based on the decomposition coeffi cients of orthoexponential functions discussed in the study.
Physics and Mathematics
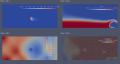
The study conducts a test and numerical modeling of fl ame front propagation along a stratifi ed gas mixture in a small transverse fl at channel made by two parallel plates. Images of the fl ame front were obtained through direct photography. A shape change was detected during the fl ame oscillatory propagation along a long channel. The distribution fi elds of temperature, gas concentration, pressure, velocity, and streamline were constructed. The simulation fi ndings have been shown to qualitatively coincide with the test fi ndings.